One of the key benefits of RPA is automating repetitive tasks, so in this section we will look at some examples of repetitive tasks and these examples will demonstrate how RPA improves efficiency in repetitive workflows. There are benefits of automating repetitive tasks with RPA bots, particularly cost savings from automating repetitive tasks with RPA.
FULL RPA Process EXAMPLE
Example 1 – “automating repetitive data entry tasks using RPA”
The most basic RPA solutions for high-volume repetitive tasks are those which are Straight Through Processing, for example where information is being copied from 1 place to another and there is no possibility of error.
Examples of these could be customer onboarding, in which information is updated from a PDF application form to a system.
In this example the PDF application form contains the following information:
- Name
- Address
- ZIP Code
- Mobile
- DOB,
- ID Passport Number

And the System contains the exact same information.
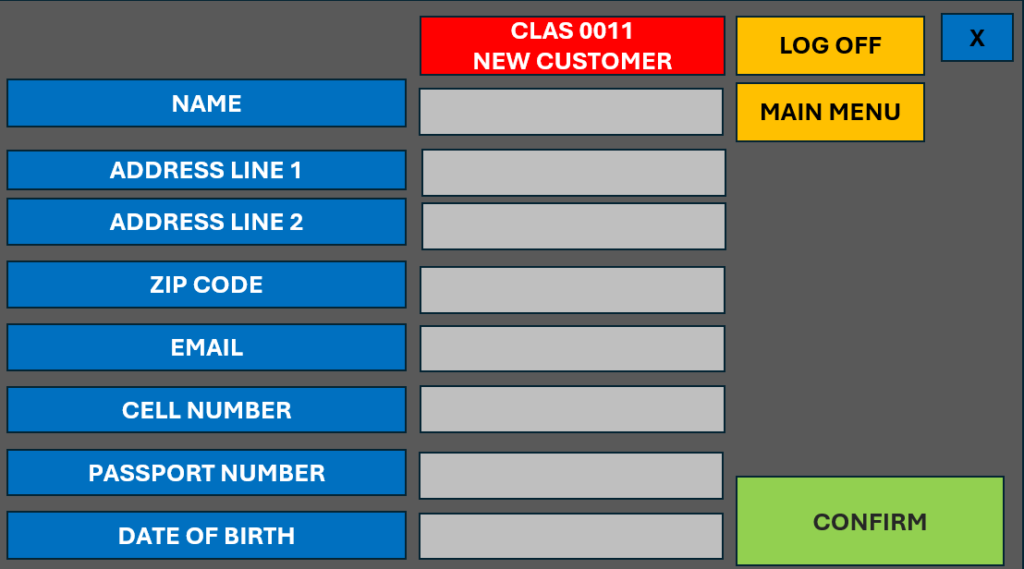
RPA has a simple task to copy from one place to the other and the only potential problem can be if customer app isn’t complete, which hopefully won’t be the case if the form contains validation which prevents it being submitted incomplete.
Example 2 – automating repetitive data entry tasks using RPA
We can now look at a more complex version of this example, in which in our experience customers believe not to be repetitive, – in which logic is required, so the perfect example of this could be, is the application single or joint.
If we look at the below process map it looks if an application is sole or joint, a decision (diamond shape) is used by the RPA Solution to assess and the process can follow 2 paths, the only difference in this example is if there is a second customer the process has to repeat adding the second customers information, and then the process rejoins the same process, this being an example of how to automate repetitive copy‑paste tasks with RPA.
Example Process Map – RPA Implementation for repetitive workflow automation
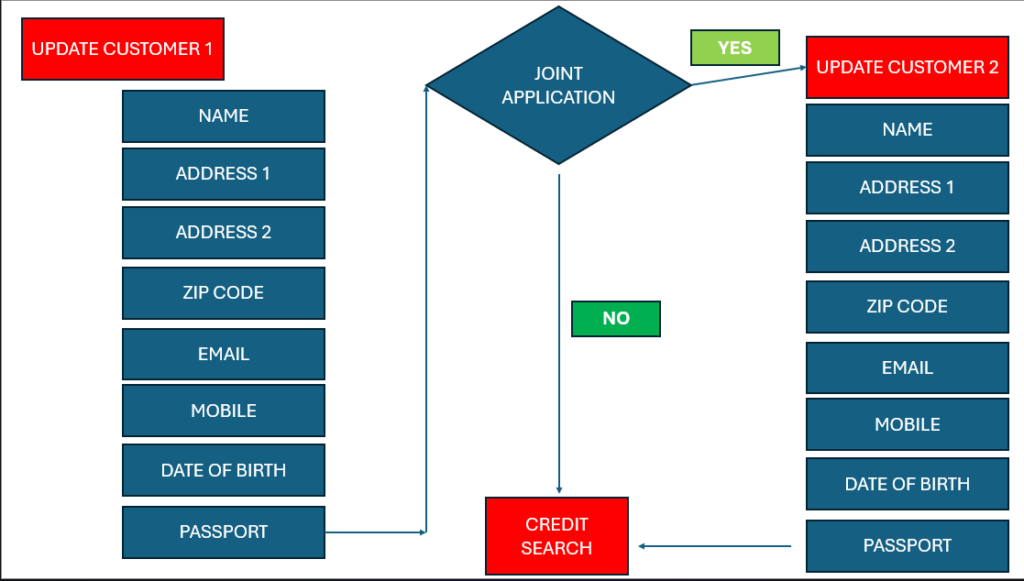
There will therefore be multiple situations where a process can follow different paths, depending on the circumstances, for example if an invoice is above or below $500 different paths are taken, if the customer has applied for 1 of a number of products, send a different email depending on if a customer application is approved or declined.
The automation can be built with rules, to handle these different paths. Different customer applications may follow different paths but as the automation handles all the scenarios these are classed as repetitive.
If the number of scenarios is so wide ranging that a customer application might generate 15 paths and these may expand into numerous other paths this can still be repetitive as it can be handled, but this is less suitable process for automation due to the amount of development time that will be required.
This is repetitive if the robot can complete this task and move onto the next customer, there is no decision making or choices to make in this automation and therefore is probably quite easy to measure the time taken for each customer, application and predict accurately the number of robots required and assess if automation is worthwhile.
For example, if the robot takes 2 minutes per application, we can estimate it can complete 30 applications per hour, and if 250 applications are received daily, 1 robot licence running for 8.5 Hours will complete the process. There are therefore likely to be cost savings from automating repetitive tasks with RPA <For more information on resourcing.
Examples of Repetitive Tasks by Industry
In this section we can look at RPA for repetitive customer service back‑office tasks and provide some brief examples of repetitive tasks by industry.
Admin and Document Handling RPA Repetitive Task Examples
| Invoice Processing (RPA for repetitive Invoice Processing in accounting) | Receiving, Validating, Coding and Entering Invoices. |
| Purchase Order Creation | Generating Purchase Orders based on requests and approvals. |
| Document Indexing | Tagging and Filling Documents into systems. |
| Contract Lifecycle updates | Versioning, Tracking Renewals, Archiving |
| Form Validation | Checking completeness and accuracy of completed forms. |
Finance and Accounting (Most common Finance and Accounting Processes automated with RPA.
| Accounts Payable Cycles | Matching Invoices Payments and Approvals |
| Accounts Receivable Follow Ups | Sending reminders, posting receipts |
| Expense report auditing | Verifying receipts and policy compliance |
| Bank reconciliation | Comparing Statements to Internal Records |
| Month-end routines | Journal entries, accruals, adjustments |
HR & People Operations (automating repetitive HR onboarding tasks with RPA)
| Employee Onboarding Steps | Account set up, Document collection, Training updates |
| Payroll Data Preparation | Hours, Overtime, Deductions, Benefits |
| Leave request processing | Approvals, System updates, Notifications |
| Compliance Reporting | Generating recurring HR reports |
| Performance Cycle Administration | Reminders, Form Collection, Tracking |